Accessibility in Web Design: Ensuring an Inclusive User Experience
As internet accessibility grows, web designers must ensure that their websites are inclusive for all users. It implies creating websites accessible for specially-abled individuals and those who may not have access to certain technologies or have slower internet connections. The Internet offers many opportunities, from shopping to socializing, learning to working.
However, for many specially-abled people, navigating the online world can be a daunting and frustrating experience. Accessibility in web design is about ensuring that websites are accessible and usable to everyone. To ensure a truly inclusive user experience, web designers and developers must prioritize accessibility.

What is Accessibility in Web Design?
Accessibility in web design involves the principles and techniques used to design websites and web applications that are accessible and navigable for all. It encompasses people with visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive challenges.
The goal is to provide equal access to information and functionality, ensuring everyone can fully participate online. However, designing accessible websites also benefits those using mobile devices or having slow network connections.
Key Principles of Web Accessibility
For the website to provide web accessibility features, it is important to follow the key principles outlined in the WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines):
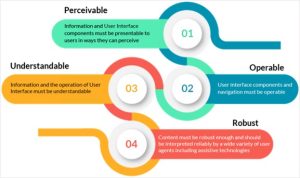
- Perceivable
It is essential to ensure that all information and user interface components are presented so that all users can perceive. It includes providing text alternatives for non-text content, such as images, and using clear and understandable text. - Understandable
Verify that information and the operation of the user interface are easy to understand. It involves using clear and consistent navigation, providing helpful error messages, and avoiding overly complex language.
- Operable
Ensure all functionality is available through a keyboard interface and that navigation and input are consistent and predictable. The feature benefits users who rely more on keyboards or alternative input devices. - Robust
Create content that various user agents, including assistive technologies, can reliably interpret. It means using valid and semantic HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build your website.
Why does Accessibility matter?
1. Inclusivity
The most compelling reason to prioritize web accessibility is to ensure that your website is inclusive. By making your site accessible, you open it up to a broader audience, including specially-abled people. It benefits individuals and helps create a more diverse and inclusive online community.
For example – Salesforce’s1 commitment to accessibility extends to all users, including those who require assistive tools such as speech recognition software and screen readers.
2. Legal Compliance
Many countries have established legal requirements for web accessibility. Failing to meet these standards can lead to legal consequences. In the United States, websites of certain organizations, like government agencies and educational institutions, are required to comply with the WCAG.
When developing a website, it’s essential to consider the following website laws and regulations:
- Data Privacy and Collection Regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.)
- Data Security Guidelines
- Accessibility Standards (ADA, WCAG, etc.)
- E-commerce Security Requirements
- Copyright and Plagiarism Rules
- Content Licensing and Attribution Guidelines
- Anti-Spam Legislation
- Necessary Disclaimers
- Cookie Compliance (GDPR, ePrivacy, etc.)
For example – Websites like BBC2 use cookies to remember your preferences and improve your experience on future visits.

3. SEO Benefits
Accessible websites have better search engine rankings, as the search engines prioritize
user-friendly websites, and accessibility is a key component of user-friendliness. Properly structured headings, alt text for images, and semantic HTML all contribute to a better SEO score.

For example – Nike4 uses the most popular keywords in its sector and bombards them all over their homepage. Starting from its introductory screen and new arrivals to trending and featured products.
4. Improved User Experience
Accessibility features often enhance the overall user experience. For example, video captions benefit those facing auditory challenges and people trying to listen to something in noisy environments or prefer reading rather than listening. Additionally, well-structured content is easier for everyone to navigate.
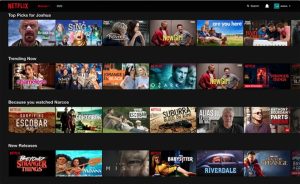
For example – Netflix’s5 website has a clear layout and personalized feature that suggests content based on previous viewing history. It improves the user experience and saves time in finding the right content.
Practical Tips for Implementing Web Accessibility
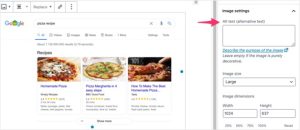
1. Use proper alt text for images
Alt text is the written description of an image that appears if the image fails to load on a webpage. Text helps optically challenged readers by describing images and improves website ranking on search engines, as shown below.
2. Semantic HTML
Structure your content properly using semantic HTML elements. Make use of headings, lists, and semantic tags like <nav>, <article>, and <aside>, to provide a clear structure to your page.

3. Provide Alternative Text
Always include descriptive alt text for images so that screen readers can convey the information to users with visual impairments. You can refer to the image below.

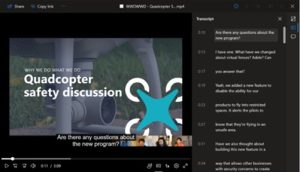
4. Caption and Transcribe Media
Transcribing audio into text format is called transcription. Captioning involves dividing the transcript text into time-coded segments, referred to as “caption frames.” Although transcription is helpful for accessibility, legally required accurate closed captions are necessary for video accessibility. Both transcription and captioning can improve video SEO.
5. Keyboard Navigation
Ensure that all interactive elements on your website can be accessed and operated using only a keyboard. It will help create a more straightforward and easier-to-use digital experience, enabling more people to continue relying on technology.
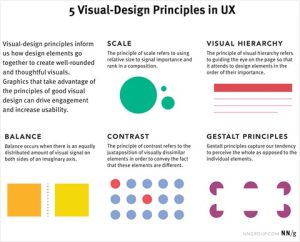
6. Colour Contrast
Maintain adequate color contrast to make text and images readable for optically challenged users. Choosing a color scheme that complements your brand’s identity is crucial when designing your website.
For instance, if your website has an environmental message, earthy tones can help reinforce that message. The website for Mandai Wildlife Reserve9 is an excellent example of this, as they use earthy colors to establish themselves as an eco-conscious brand.
The color scheme for their wildlife eco park website includes dark green, ivory, and yellow, commonly associated with nature. This palette creates a calming and organic ambiance for the website, making it pleasing to the eye.

7. Testing
Regularly test your website for accessibility using tools and involve specially-abled users in usability testing. The feature will improve website ranking, design, and backlink potential.
Takeaway
Web accessibility is not just a nice-to-have; it’s an essential aspect of web design and development. By ensuring that your website is accessible to everyone, you comply with legal requirements and contribute to a more inclusive and user-friendly internet. Remember that accessibility is an ongoing process, and it’s crucial to stay informed about evolving standards and technologies to ensure that your website remains accessible to all and creates a digital world that embraces diversity and inclusion. So, when designing or revamping your website, remember that accessibility is not just an option—it’s a fundamental requirement for a more equitable online experience.
At V2Solutions, we’re your trusted Digital Transformation partner, focused on delivering innovative solutions and compelling content that empowers your brand. With our deep knowledge of digital trends, we’ll keep your brand ahead of the curve, giving you a competitive edge in the ever-changing business landscape. Let’s work together to unlock your brand’s full potential, explore new strategies, and create resonant content for growth and success.